|
8 Administration
In SysMT, all administrative tasks SysMT can be done in the admin menu panel. This includes user and group management but also system set and thread group management. Furthermore, interface configuration to attached systems is managed here.
8.1 Business Groups
SysMT uses a powerful grouping concept which allows to customize a restricted access for each user to the managed data. In this sense, a SysMT user is assigned to on or more business groups. So the user view is restricted to the objects, which have been assigned to the corresponding group.
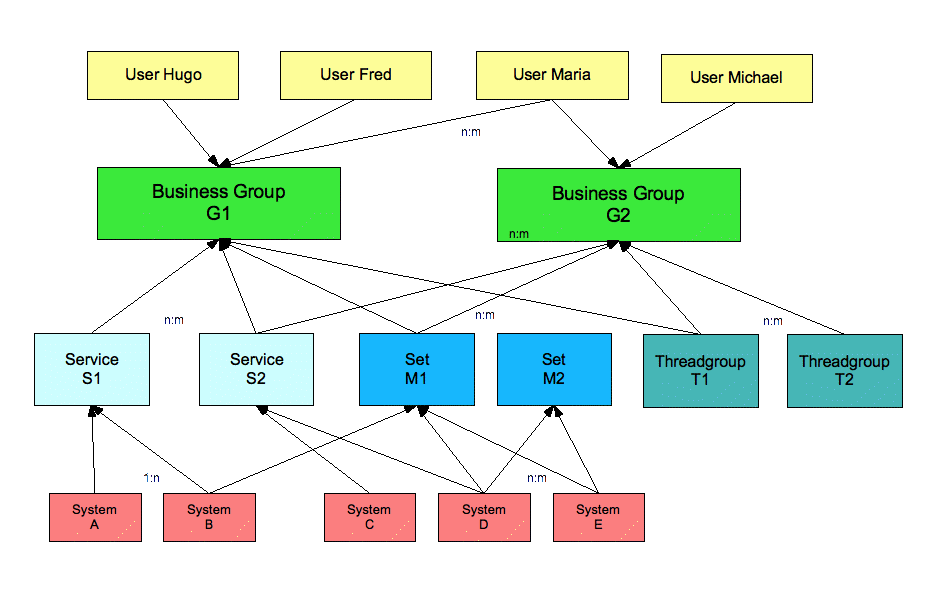 |
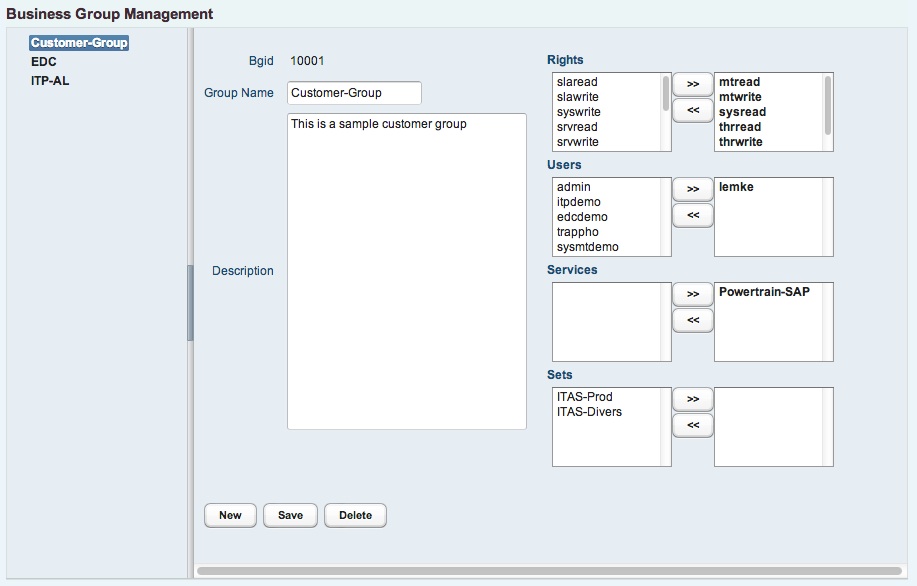
To each business group , several role attributes are assigned to define, what business objects can be accessed in which way.
- devread - Read device information
- devwrite - Write device information
- catread - Read service catalog information
- catwrite - Write service catalog information
- mtread - Read maintain information
- mtwrite - Write maintain information
- sysread - Read system information
- syswrite - Write system information
- srvread - Read service information
- srvwrite - Write service information
- slaread - Read any SLA data
- slawrite - Write any SLA data
- thrread - Read and write any thread data
- thrwrite - Read and write any thread data
- resread - Read resource planning data
- reswrite - Write resource planning data
Based on this concept, approprate business groups can be defined and users, services, system sets and thread groups can be assigned to it.
 |
8.2 Users
Users are managed in SysMT using the user management panel.
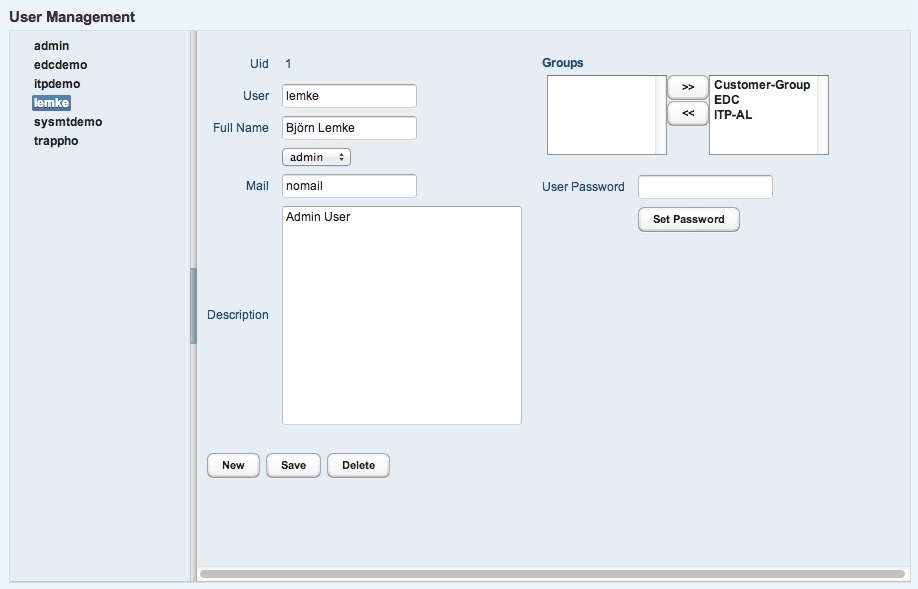 |
The user can be assigned to normal or admin role. If the user get admin rights, he is authorized for all administration activities.
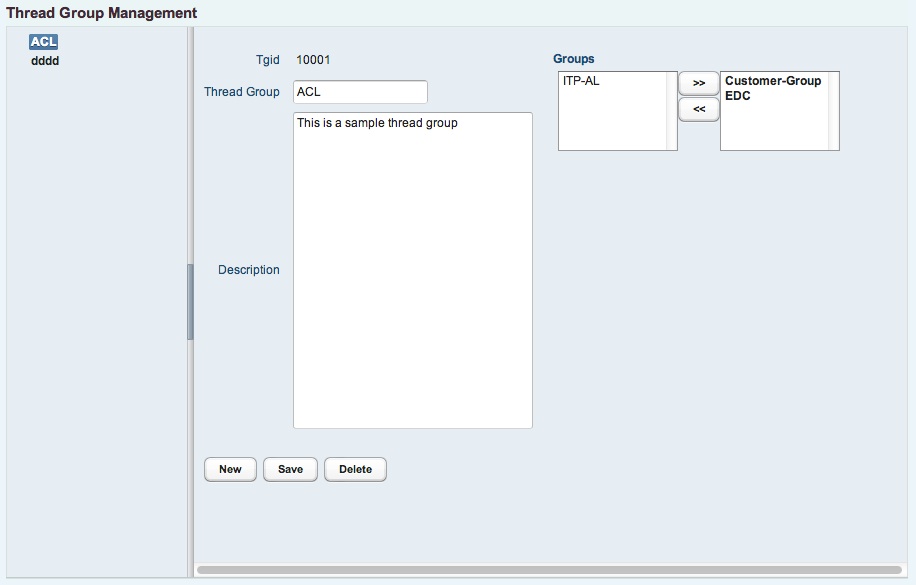
8.3 Thread groups
The thread group master mask
 |
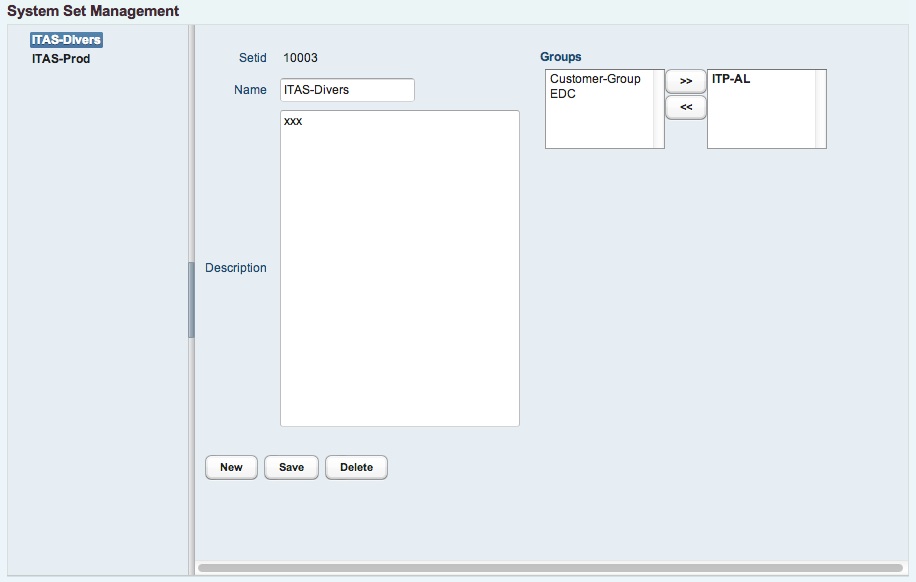
8.4 System sets
System sets can contain a set of systems
 |
8.5 Filesystem templates
still not implemented
8.6 Group search
still not implemented
8.7 Others
8.7.1 MID Release
If a user has claimed a maintain entry, the entry is locked until the user confirms or aborted his changes for the entry. A lock removal can be forced by the administrator using the MID release feature.
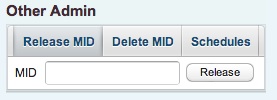 |
A sucessful lock release is indicated by a corresponding information box. Otherwise, if the mid does not exist or if the given number format is not correct, an error box is shown.
8.7.2 MID Deletion
Since it is not allowed for a normal user to delete any created maintain entry, wrong or obsolete entries have to be removed by the administrator. To remove a maintain entry, the corresponding mid has to be inserted.
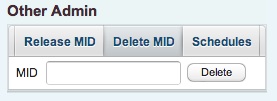 |
A sucessful deletion is indicated by a corresponding information box. Otherwise, if the mid does not exist or if the given number format is not correct, an error box is shown.
8.7.3 Scheduler
The SysMT internal scheduler allows to execute any batch job in a periodic manner. Batch jobs can be either standard programms or customer specific extensions. Any job has to be implemented as a derived class of SysMTScheduleThread and it is executed by the scheduler as a dedicated java thread.
For the schedule administration, the job program is registered in the admin scheduler section.
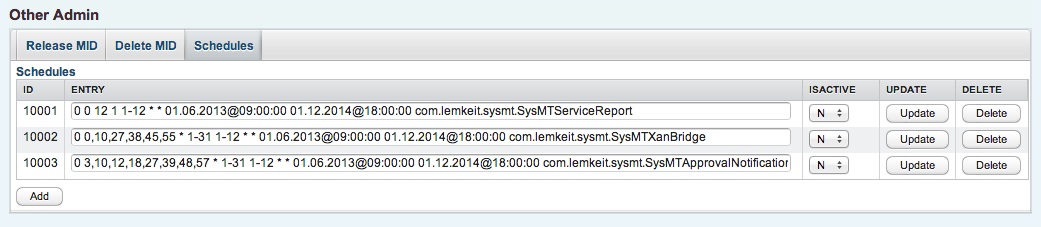 |
A scheduler entry contains a unique numeric schedule id and a crontab like defintion with space separated fields
- Seconds
- Minutes
- Hours
- DaysOfMonth
- Months
- DaysOfWeek
- Year
- StartDate
- EndDate
- Classname
The wild card token * selects the complete range, smaller ranges can be specified with the - token. Dedicated values are separated by a , token. For the classname specification , the following classes are available
| Classname | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| com.lemkeit.sysmt.SysMTServiceReport | Standard | Customer status report with some statistics information |
| com.lemkeit.sysmt.SysMTXanBridge | Standard | Xandria Bridge Interface for information propagation |
| com.lemkeit.sysmt.SysMTApprovalNotification | Standard | Approval reminder job |