|
| 4 Service Management |
|---|
| Back to TOC |
The service management module provides a rather business oriented view and corresponding functions to the managed data. It is normally used by service or SLA managers or by the service customer. IT services can be designed and ordered, the corresponding SLA information is internally managed by the system and informs about the incurred cost.
4.1 Service Catalog
The service catlog contains all planned or available service modules which should be provided to the cusomers. In this sense, SysMT supports the ITIL service design process as an early step in the whole service life cycle.
To understand SysMT service modules, it is important to know about about the system structure. A system consists of several system instances, wher each instance allocates a number of CPU, memory and disk resources. Furtermore systems are configured in a service type context. The service types describes the kind of application, that delivers the corresponding service. Actually, SysMT supports the following service types
- SAP
- PeopleSoft
- Native Database
- Web Service
A service module either contains a complete system, a system expansion or an instance expansion. Initially, a complete system should be ordered by a customer and later on, further system instances can be added, or a system instance can be expanded to assign further cpu, memory or disk resources.
4.1.1 Creating a catalog entry
As a result of the service design process, a corresponding service catalog entry is created. The catalog entry describes the scope of the service in terms of function and price. A catalog entry can include a complete system or just the extension of an existing system. Each catalog entry is usually that created by the SLA team in consultation with the technical design team.
If a new catalog entry is selected, the following mask appears.
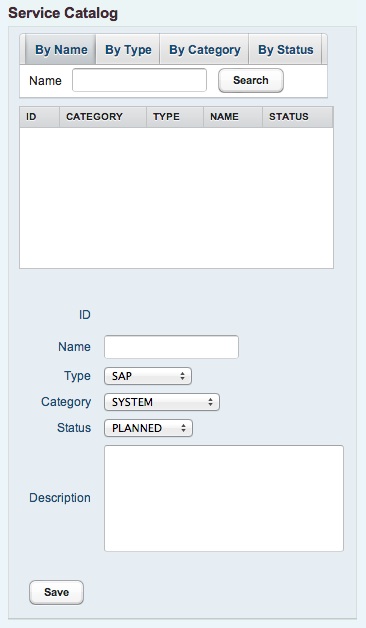 |
The new catalog entry is identified by its unique name. It is recommended to use a naming convention for catalog entries according to the specific organisational requirements.
Next, the of category should be defined. This is either SYSTEM, SYSEXPANSION or INSTEXPANSION depending on if the new entry should describe a complete system or just an system or instance expansion.
The service type describes the application context, for what the catalog entry is designed for. Actually, SAP, PeopleSoft, DB and WEB application types are possible.
The description field can used for any further detailed description of the catalog entry.
If the new catalog entry has initially creates, component types can be assigned to it.
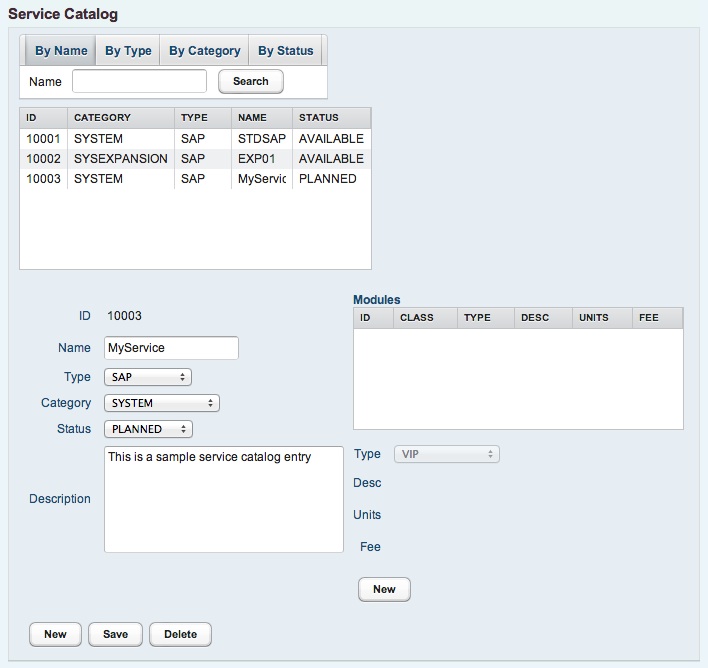 |
The component type list of a catalog entry describes the sizing of a system or an expansion. The following component types can be configured.
- CPU - CPU resource
- MEMORY - Memory resource
- DISK - Disk resource
- VIP - Application service with virtual adress
If a component type is added to a catalog entry, further information should be given about the amount and price.
If entries have been created, they can be changed or deleted later on. In the following, the catalog entry for a SAP system is illustrated.
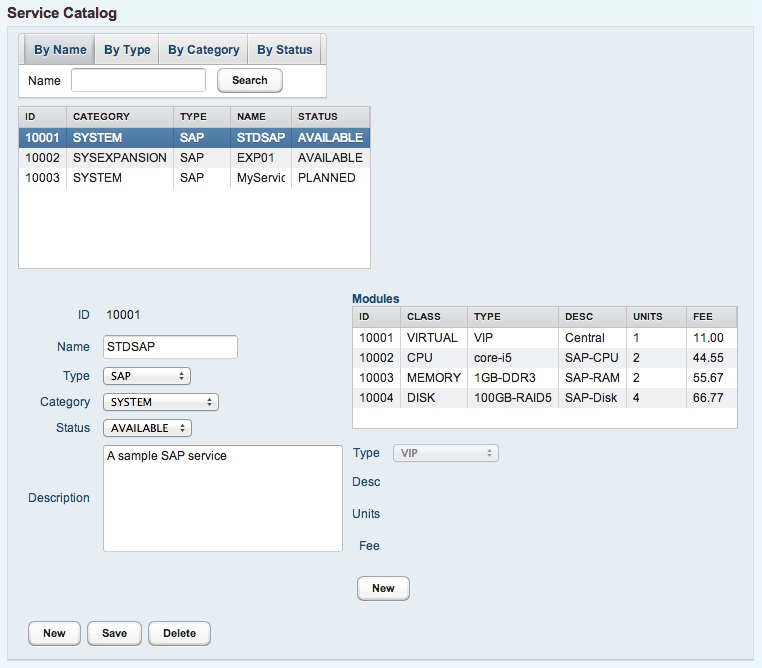 |
To make the catalog entry available for ordering, the entry status has to be changed to AVAILABLE
4.2 Service Level Agreement
SLA are the base to measure and account any services for a customer. Normally, one SLA is created for each customer and a couple of services are assigned to it.
4.2.1 Creating a SLA
To create an SLA, an appropriate name must be specified. Further, a description could be provided in the textfield.
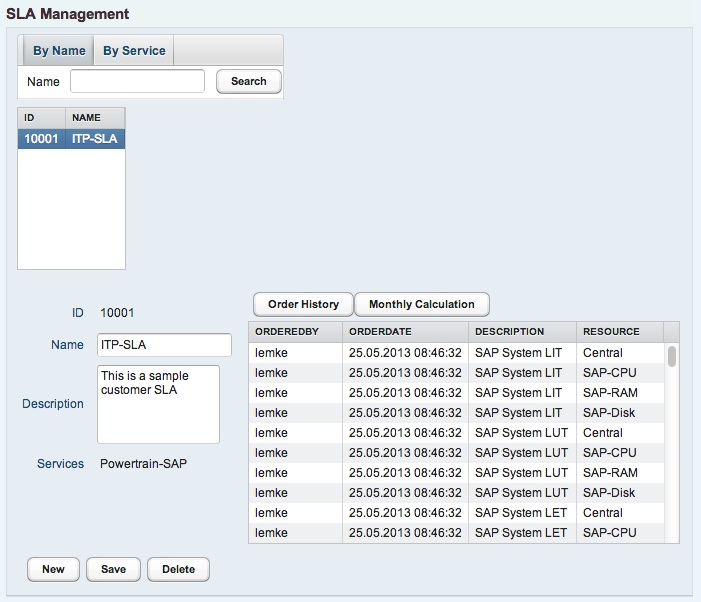 |
To an existing SLA, any customer services could be assigned. Since this is an 1:n relation, services are always dedicated to one customer.
4.2.2 Order Information
The order history logs each ordering process and gives information, who has ordered which component at what time.
4.2.3 System calculation
The system calculation gives an overview about the resulting costs for each accounted system.
4.2.4 Monthly calculation
The monthly calculation gives a cost overview for all accounted systems on a monthly base.
4.2.5 Deleting a SLA
The deletion of a SLA should be an exception. This results in a cascading deletion of all corresponding services and systems.
4.3 Services
Services are provided by the IT-Service provider to its customers. In SysMT, a service is always in context with an application type and other properties described for the corresponding service.
4.3.1 Creating a service
Services are created via the service panel. It is recommended to use appropriate names for new services following a naming convention.
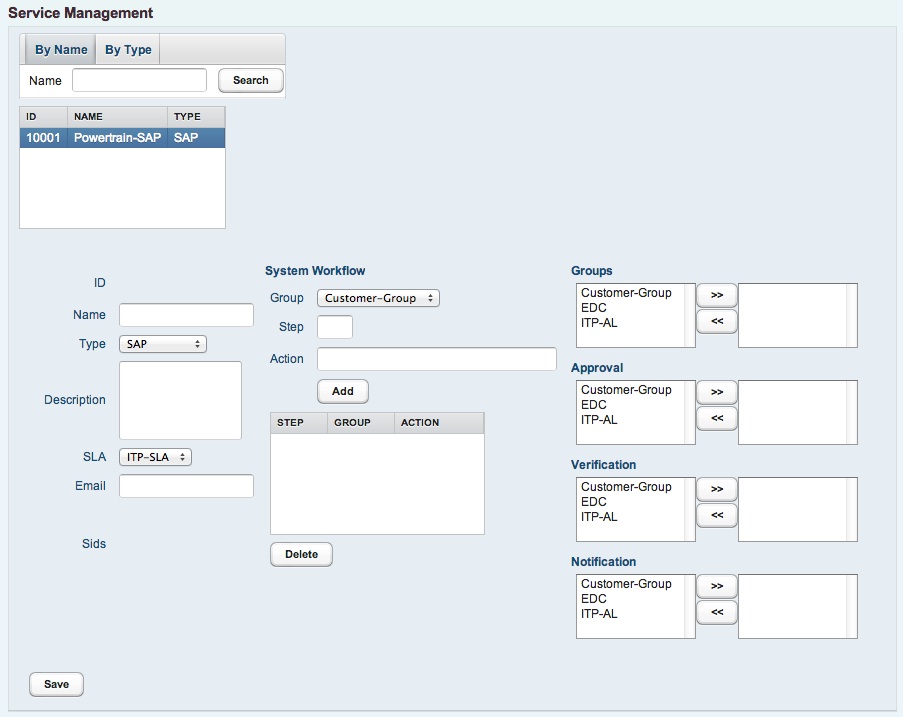 |
Any new service has to be assigned ot a valid SLA.
4.3.2 Service configuration
Within the service, different processes are implemented and executed during the build and run phase. For this, an appropriate service configuration has to be done.
4.3.2.1 System build process
The system build process is designed to ensure a well defined and efficient system deployment. During the build process, a system goes through several phases. The build phases are described with workflow steps. To each workflow step, a number is assigned indicating the ordering of each steps. It is allowed to give a same number to several workflow steps. In this case, the corresponding workflow steps can be implemented in parallel.
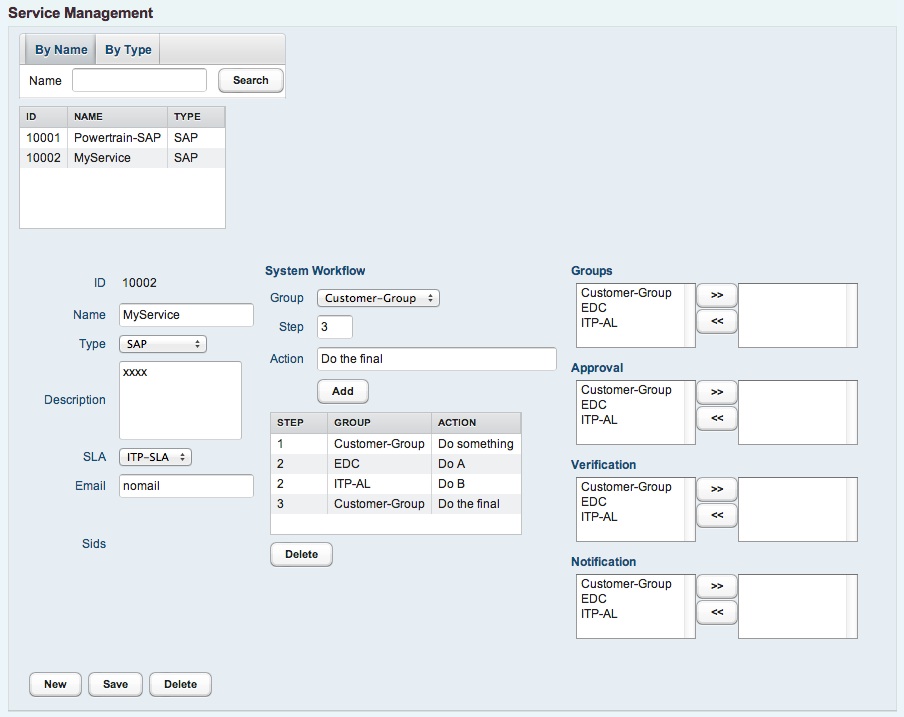 |
All systems for the corresponding service are build using the above described workflow. The system build workflow itself is discusses later in the the system management section.
4.3.2.2 Business groups
To make a service accessible for users, it must be assigned to the corresponding business groups. Normally, the service is assigned to a provider and a customer group.
4.3.2.3 Approval
The maintain approval process is customized in a way, that the involved buisness groups are added to the process. During the approval, any member of each group has to approve the maintain entry to change it to approved state.
4.3.2.4 Verification
As same as for maintain approval, the maintain verification can be customized. Several business groups can be added to the verification process which are requested to verify the result of the maintain implementation.
4.3.2.5 Notification
Still not implemented
4.3.3 Deleting a service
If a service is deleted, all dependent business objects are deleted too. This includes the existing system entries and the maintain entries for each of these systems. A deletion of a service should be done very carefully.
4.4 Ordering process
New systems or system expansions are added to an existing service using the ordering process. First in this process, all required resources are checked for availability. If all resources are available, they are allocated and assigned to the corresponding system instance. In this sense, the ordering process keeps the device, sytem and service information in a consistent and current state.
This method leads to an highly automatic ordering and deployment process for datacenter systems. As a consequence, cost reductions and qualitity improvements are the result.
4.4.1 Ordering a service
Any available entry from the service catalog can be ordered to the appropriate service. Basically for each service type, a complete system, a system expansion or a instance expansion could be ordered. The required resources including prices are listed in the table below The device selection allows to assign the required components to one of the devices provided in the selection. Just those devices are provided, which have the corresponding resources available. Later on in the system management panel during the subsequent build process, components could be reassigned to different devices, if necessary.
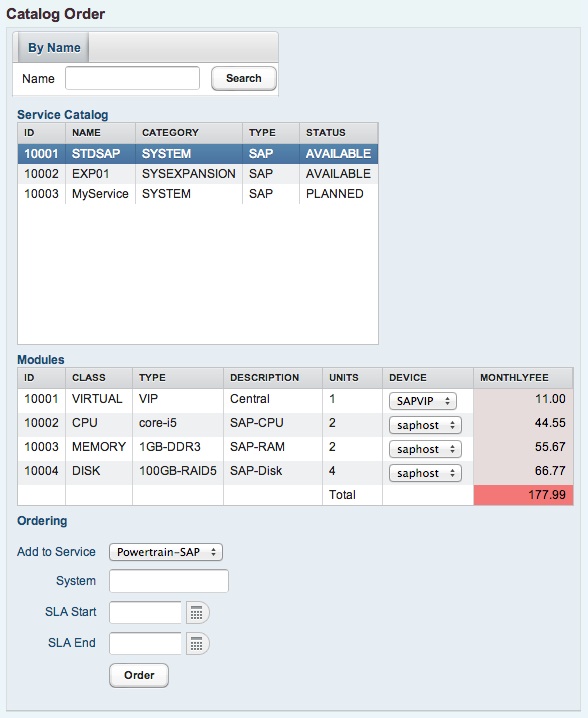 |
To order a system, a unique system identification has to be defined for the system. The system identification is a string value and can be defined regarding to the corresponding application context. For SAP systems, the system id could be defined as same as the SAP SID ( If SAP SID is unique inside the organization )
If a new instance should be ordered to an existing system, just the instance suffix must be defined. This can be any kind of alphanumeric identification ( e.g. SAP instance nr ).
Since for instance expansion resources are just added to an existing instance, just the corresponding instance has to be selected.
The duration of the service also must be specified. In accordance to the SLA regulations, this might be from one month up to three years or more.
Finally the order is started pressing the order button.